- Front Case Fan Not Spinning: [3 Proven Fixes That Work - June 22, 2022
- Is 60 Degrees Celsius Hot For A CPU In 2022? [Must-Read] - June 7, 2022
- How To Handle CPU Temps Jumping: A Definitive Guide [2022] - June 2, 2022
A computer is a system of interconnected components that work in a given order to showcase any function. And if you are interested to learn in detail about it, then there is a term that you would come across- PCI.
Abbreviation for Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI defines the hardware bus through which different controller cards are connected to the motherboard of the computer/laptop. These connections are defined through standardized pins that are independent of the brand, and allot fixed addresses in the processor’s space.
What started as 32-bit and PCI-X version eventually metamorphosed to PCI Express (PCI-E) and then 64-bit. And the placement of the cards in their respective slots is very important- else they would get damaged with the power supply.
Thus, in today’s article, we would be focusing on what is PCI latency timer, and how does it impact the overall performance of the system.
Contents
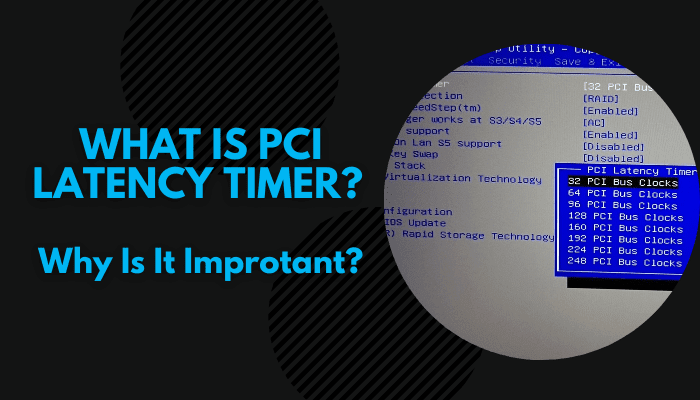
What is PCI Latency Timer?
PCI Latency is an important factor that shows how long would any device or controller hold on to the bus, before transmitting into another device. Also called a timer in some terminologies, the value goes between 0 to 248. Zero means that the device would not stick to the bus and immediately give up when another transmit is received, whereas 248 means that it would stick to the bus in the longest possible period.
The higher value of the PCI bus latency timer indicates greater bandwidth due to the reduced overhead of transferring between devices.
32 Cycle: What You Need to Know
32 cycle is the default PCI Latency timer for your device connected to the bus. In simple terms, it means that the active device has to complete its transaction within 32 clock cycles, before going as handover to the next PCI device.
This is considered as one of the ideal cycles, as there would not be a long queue of stalled devices waiting to use the bus, and hence keeps up with the required performance of the computer.
64 Cycle: What You Need to Know
64 Cycle is recommended for those systems where you want to take the performance to the next level. This may be the optimal value for some systems, and you should benchmark the device performance with each latency increase before finalizing on any value.
This is regulated by BIOS feature Secondary Lat Timer and sets the PCI transaction through hex codes (The one for 64 being 40h).
128 Cycle: What You Need to Know
128 Cycle is the next level from 64 cycles, which is recommended for some of the cards that are involved in high-performance activities like gaming, working on any design software, setting up a network, etc. Just like 64 cycles, this timer also needs to be checked before finalizing on any device.
The hex code for it is 80h.
You can easily change the latency timer values through the below command:
setpci -v -s xx:yy.z latency_timer=[n]
The Default PCI Latency Timer
Whenever you would come across any PCI driver, you would find its default latency timer at 32 cycles or 20h. This means that the bus’s PCI-to-PCI bridge has to complete 32 clock cycles before transmitting to the next device. This value is generally considered optimal for those users who work on the basic operations with their computers.
If you want to boost the timer for gaming, then try going for 128 cycles and higher. (Refer to our article clock speed vs cores for gaming to gain a better idea).
How Does PCI Latency Timer Boost PCI Bandwidth?
BIOS PCI Latency Timer is a setting that regulates the I/O processing of the computer. And this is the value that controls the bandwidth of operation for the computer.
For example, under the 32-bit version running at 33 MHz or 66 MHz, the bandwidths observed are 133 MB/s and 266 MB/s. For the 64-bit version at 66 MHz, the same value goes up to 532 MB/s.
Therefore, the relationship is directly proportional to the bandwidth, i.e. higher timer value means greater bandwidth of operation. It goes into real application in the following ways:
- The existing bus prioritizes the operation of the connected devices in a manner that the ones critical to the performance and go compatible with the higher timer values stay and operate the system.
- The boost works well while using extension cards in the PCI connector, and configuring the same with the Operating System.
The only catch over here is the compatibility of the device connected to the bus with higher latency timers. Be very sure of doing your research before playing with these values.
Is Longer PCI Latency Better for Your PC?
First of all, you should remove the misconception from your mind that longer PCI Latency is mandatorily better for the PC. It is true only if the PCI controller connected to the computer bus has compatibility with a higher timer for the interface device. Otherwise, the longer values can slow down the performance in the following ways:
- Other devices get queued up in the line and may get stalled for long hours.
- The devices that aid in short bursts of read/write data to the computer would get affected, and hence you would find frequent crashing at multiple settings.
- The priority access would get disturbed, and therefore the time-critical PCIs would fail under the enhanced values.
So, it is highly recommended that you should not move out of the default 32 cycles unless there is another critical activity that needs to be run parallel. This issue is observed mostly with RAID controllers, where the RAID value and Latency timer do not match.
Are All PCI Devices Compatible with Long Latency Timer?
No, all PCI devices are not compatible with long Latency timers and keep varying as per the manufacturer’s specifications. In general, the older versions of PCI that were developed some 20-25 years ago were meant for working only in 32 cycles and could handle at max 5 devices.
With time, new generations like PCI Express 5, Express 4, X came into existence and they allow to be configured at the higher latency timers. Such value for PCI Express allows speed-boosting for the following applications:
- AI, ML, and cloud-based applications.
- High-speed networking protocols.
- Duplex transceiver like PCI-E lane.
- PCI latency timer for data mining activities.
The data transfer rate in PCI-e 5 is twice that of PCI-e 4 and can hence support the applications mentioned above.
List of Compatible PCI Devices
PCI Express 5
PCI Express 4
PCI-X Devices
List of Incompatible PCI Devices
- PCI 1.0
- PCI 2.0
- PCI 2.1
- PCI 2.2
- PCI 2.3
- PCI 3.0
Does PCI Latency Timer Affect The GPU?
There is no direct correlation between PCI Latency Timer and GPU. When it comes to the computers that are equipped with the latest generation of PCI or GPU, there would not be any incompatibility as they are configured to function well even at the higher cycles.
For the older versions, the optimal value needs to be set on a hit and trial basis. If your PCI device is set to a higher timer and does not complete its activity before transmitting to another device, then you may hear unwanted noises from different cards. This means that the devices which require frequent bus access get overflowed with buffer times and lose data.
Therefore, if you are using an excessively old GPU, then you may observe some impact.
FAQs
1. What does PCI Latency timer mean?
PCI Latency timer is a BIOS feature that controls how long would any PCI device stays connected with the system bus before transmitting to another device. In simple terms, the longer the value, the higher would be the retention power with the bus.
2. What is the best setting for PCI Latency Timer?
The default value for PCI Latency Timer is 32 cycles. It goes well if your system has basic to moderate types of applications, and would not require any upgrade on the stock configuration. But if you want to work on any high-performance activity, then consider going for 64 and 128 cycles.
3. What is the PCI latency timer in BIOS?
As mentioned previously, the default timer is 32 cycles. If you want to boost the value, then you can do so by using the appropriate syntax in the BIOS command prompt.
4. What should my PCI latency timer be set at?
There is no defined PCI latency timer. It all depends upon your device configuration and applications. If it has PCI Express 5, then you can think of going all the way to 248 cycles. Check the manufacturer’s guide for more details.
5. What does the PCI latency timer do?
PCI Latency timer defines the duration for which the device stays connected to the system bus. As a result, there is a fixed constraint for the device to complete the activity before switching to others.
Final Words
On an ending note, PCI Latency Timer is quite important for those who want to understand better about a computer’s performance. The different cycle times determine the active period for each of the devices connected to the bus and accordingly process the I/O cycle.
Any undesired configuration boost can cause frequent crashing. Therefore, it is very crucial to understand the terminologies, and not get swayed away by the misconception that a higher cycle brings higher performance.
Keep swiping our website for more of such related articles, like ‘What is NB frequency?’, ‘Is pc2 the same as ddr2?’ and many more.

![Best Mousepad For High DPI [7 Amazing Picks Reviewed] Best Mousepad For High DPI [7 Amazing Picks Reviewed]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/best-mousepad-for-high-dpi-150x150.jpg)
![Best CPU For Programming In 2022 [7 Picks For Every Budget] Best CPU For Programming In 2022 [7 Picks For Every Budget]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/best-cpu-for-programming-150x150.jpg)
![How To Change CPU Fan Speed Without Bios? [Easy Guide] How To Change CPU Fan Speed Without Bios? [Easy Guide]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/How-To-Change-CPU-Fan-Speed-Without-Bios-150x150.jpg)
![Best CPU for Minecraft In 2022 [7 Worthy Picks Reviewed] Best CPU for Minecraft In 2022 [7 Worthy Picks Reviewed]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/best-cpu-for-minecraft-150x150.jpg)

![Best CPU For Multitasking In 2022 [Based On Expert Opinion] Best CPU For Multitasking In 2022 [Based On Expert Opinion]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/best-cpu-for-multitasking-150x150.jpg)