- Front Case Fan Not Spinning: [3 Proven Fixes That Work - June 22, 2022
- Is 60 Degrees Celsius Hot For A CPU In 2022? [Must-Read] - June 7, 2022
- How To Handle CPU Temps Jumping: A Definitive Guide [2022] - June 2, 2022
Laws of Physics are bound by everything that happens around the world. Something similar is also the case with computers. Whenever it comes to talks on high performance, you would also get to hear discussions on heat dissipation, temperature, and similar thermodynamic concepts.
With the electronic revolution, now the work has been eased by sensors at appropriate locations. You would also find one within the motherboard that senses the temperature of the overall CPU. It is called CPUTIN.
In today’s article, we would be covering the basics of ‘What is CPUTIN?’, how does it work, interpretation of the results, and finally the indications provided by it on PC health.
Contents
What Is CPUTIN or CPU Temperature Index?
CPU Temperature Index, popularly called CPUTIN is the reading highlighted by the temperature sensor present in the motherboard. As the motherboard controls a majority of the computer functions, it is imperative to maintain its temperature as per the specified limits
On average, the working temperature is considered as 40-50 degrees celsius, whereas the maximum can go up to 70-80 degrees. Once it exceeds 90 degrees, the system starts throttling, and it becomes a serious concern for the users. Hence, we are reiterating – please keep an eye on the safe temperature of CPUTIN in BIOS settings.
Value, Min, and Max- What Do They Mean?
If you would have noticed, the sensor displays three types of readings in the table
- Value- The current temperature reading highlighted by the sensor is based on real-time calculations.
- Min- The minimum value when the CPUTIN sensor has been running.
- Max- The maximum value when the CPUTIN sensor has been running.
These values are also segregated into cores, as you can see the row heading with its corresponding core value. In addition, they keep on changing basis the kind of load applied on them. Refer to a similar article- What is thermal margin?
If the cores are idle i.e. without any load, then the temperatures would be at the minimum side. When the loads are applied gradually, the values increase and reach the saturation point when the system has reached the throttling position (otherwise called an overclocked stage).
It would not be wrong to say that value, min, and max also highlight the overall system stability and safety of operation. You need to worry only about the higher temperature value of CPUTIN, as it showcases the breakdown point for your PC and pinpoints the status of the cooling system.
In fact, a common root cause of a popular problem – PC keeps restarting before BIOS is overheating. CPUTIN value provides a good measure of CPU temperature.
Where Can You Read or Find CPU Temperature Index Data?
There are multiple ways of finding CPU Temperature Index Data. Swipe the next section to gain a beautiful insight.
From BIOS setting
- Open the Windows Taskbar at the lower-left corner of your PC screen.
- Go for Settings button🡪Update & Recovery🡪Recovery.
- Go to Advanced Setup and click on restart now to reboot the system while putting some constraints.
- Select Troubleshoot🡪Advanced options🡪Restart.
- Now the system would enter BIOS mode and display all necessary parameters, including checking your PC temperature.
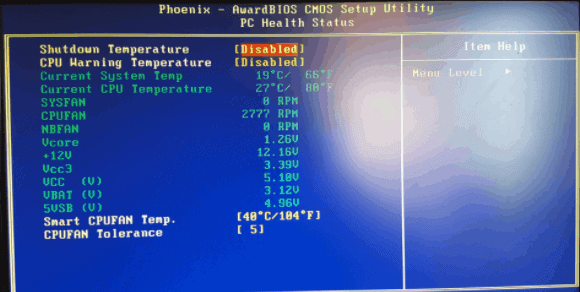
With this method, you would not be required to pay an extra subscription fee or fall into the trap of dubious softwares. However, it is a time-taking process and involves a series of constraints as specified above.
From softwares
In today’s time, several independent monitoring softwares help in displaying the core temperatures without any hassle. Some of the popular ones include the following:
- HWMonitor, which is available in both paid and free versions and allows accessibility with crisp information.
- CoreTemp, which allows customizations by the developers for adding their features.
- Open Hardware Monitor, which offers a streamlined interface for recording different readings.
- NZXT Cam, which is popular amongst gamers for recording temperature values during gaming or even overclocking.
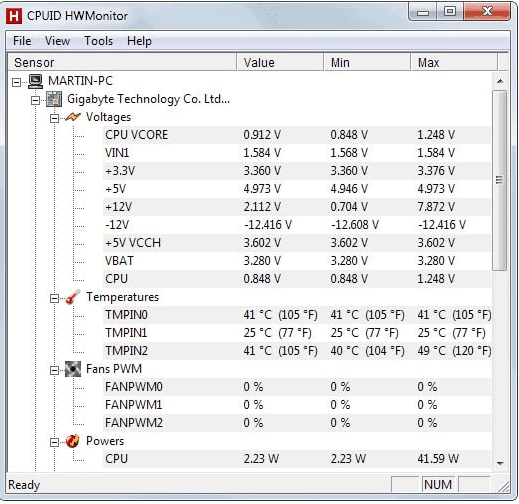
The steps are very easy, and the processing time is scaled-down when compared to the BIOS method. The values keep changing on a real-time basis, instead of staying static, and thus you would gain better insights while checking PC performance.
The only downsides are initial costs for investment in buying the subscriptions, and careful selection of the third party to avoid fraud.
Significances of CPUTIN Regarding Your PC Health
As CPUTIN indicates the motherboard temperature sensor readings, it would not be wrong to say that they help in providing good details on PC health check-ups. The following lay down the significant points that could be inferred from such observations:
- The readings highlight the ideal CPU or PC temperature within which the system stability is maintained. For example, if the value, min, and max stay within 60 degrees Celsius, then there is nothing to worry about. The cooler temperatures indicate decent PC health and life. But, the moment either of the values exceeds the above threshold, say 80 degrees, then it becomes a point of concern.
- The readings in a higher range indicate chances of overheating either within the CPU or accessories. Such values signify different reasons for which they are displayed, like as follows:
- Poor ventilation due to dust getting accumulated at intricate or critical corners of the PC.
- Old hardware setup that has lesser tolerance value to heat and temperature changes.
- Thermal paste and other accessories getting worn off with time.
Accordingly, you can work on the counter-measures to mitigate such challenges- like regular cleaning schedule, upgrading the cooling system, improvising airflow conditions, and many more.
- CPUTIN values also highlight implicitly the maximum limit up to which overclocking can be done. As there is a high risk in exposing the system to a maximum temperature, you would understand the pre-requisites and necessary hardware changes before proceeding in the process.
Many user guides highlight the correlation between CPUTIN readings and overclocking limit. You may go through those to gain better ideas.
The moral of the story states that you should take these observations seriously, and interpret CPUTIN as per specifications to avoid premature system damage.
Is CPUTIN Different from AUXTIN?
Yes, CPUTIN and AUXTIN are different and their values indicate different aspects of PC performance and health.
AUXTIN- Auxiliary Temperature Index
CPUTIN is related to the temperature sensor reading displayed within the motherboard, whereas AUXTIN refers to the sensor put in the power supply by the manufacturer. Thus, you can identify the key differences between the different locations where these sensors are placed.
By looking at the readings of AUXTIN, you can gain an idea of the stability of power or voltage drawn by the system. If the values exceed the threshold ones, then probably it will be wise to turn on the task manager and shut down all of the activities that are putting excessive load (like continuous gaming, background activities, and even lowering the parameters set for overclocking).
Is CPUTIN Different from SYSTIN?
Yes, CPUTIN and SYSTIN are also different and correspond to the readings shown by multiple sensors placed at these locations.
SYSTIN- System Temperature Index
SYSTIN indicates the actual motherboard temperature, and you can find some differences between the readings shown in CPUTIN. As the motherboard processes a good amount of information for the system, the loads keep varying on a real-time basis. Thus, SYSTIN keeps changing every second and you may have a look at its plot to understand the variations.
There is a catch to SYSTIN- not all high-temperature readings indicate some issue in the system. For example, in many high-end motherboards of ASUS, users have complained about higher SYSTIN values and the root cause has been identified as some persistent bug.
Thus, seek professional help if you are unable to decipher the problem yourself.
Is CPUTIN Different from CoreTemp?
The answer to one of the most confusing questions on CPUTIN vs Core Temp is quite simple- they are different. Core Temp is the reading shown by the temperature sensor fitted within the processor of the PC.
As per Intel processors, Core Temp defines the actual temperature with which a CPU has to deal with. It considers only the processor and not the accessories associated with it, stating that only the load given to it during high-end activities like gaming, software downloads, and others are considered.
There would not be any major impact on this reading when the system would be undergoing the procedure of overclocking. In simple terms, the differences between CPUTIN vs CPU temp lies solely due to components considered by the sensors.
FAQs
What is CPUTIN in HWMonitor?
HWMonitor is third-party software that showcases critical system parameters in a quick view. CPUTIN is one of the parameters under it and stands for CPU Temperature Index. It refers to the sensor readings present in the cores of the motherboard and highlights overall performance and health.
To have a better user understanding, the observations are shown as a value, min, and max.
CPUTIN vs package temp- which is what?
The answer to CPUTIN is mentioned in the article. When it comes to package temperature, the reading corresponds to the on-die thermal probe present on the processor. Just like CPUTIN, you can also find this reading in BIOS settings.
But, no defined literature suggests a relation between overclocking and package temperature.
What temperature should CPU be?
It depends upon the manufacturer. On average, the working temperature is considered to be within 40 to 60 degrees. Within this range, there is nothing to worry about.
If the range goes till 70 to 80 degrees, there is something to worry about as they are the higher ranges of manufacturer-specified temperature. Going beyond 90 degrees is a danger, as the system starts throttling and you would experience lags, sudden shutdowns, and other unnecessary system hindrances.
Final Words
Thus, the final verdict states that CPUTIN is a critical parameter in deciding PC health, performance, and status during high-performance activities. The readings can be observed from multiple sources- be it BIOS, or third-party apps. But the underline suggests that you cannot overlook these observations.
Whenever you find any variations, you must look for the root causes and mitigate those before the system fails drastically. And yes, they should not be confused with similar terms like SYSTIN, AUXTIN, CoreTemp, and others. They are temperature sensor readings but are located in different positions of the system.
Keep reading our website for more of such contents- like Can I use 1600 ram in 1333, What to do after installing a new motherboard, and many more. Till then, happy reading and stay safe!

![Best CPU For Programming In 2022 [7 Picks For Every Budget] Best CPU For Programming In 2022 [7 Picks For Every Budget]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/best-cpu-for-programming-150x150.jpg)
![Best Mousepad For High DPI [7 Amazing Picks Reviewed] Best Mousepad For High DPI [7 Amazing Picks Reviewed]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/best-mousepad-for-high-dpi-150x150.jpg)
![How To Change CPU Fan Speed Without Bios? [Easy Guide] How To Change CPU Fan Speed Without Bios? [Easy Guide]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/How-To-Change-CPU-Fan-Speed-Without-Bios-150x150.jpg)
![Best CPU for Minecraft In 2022 [7 Worthy Picks Reviewed] Best CPU for Minecraft In 2022 [7 Worthy Picks Reviewed]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/best-cpu-for-minecraft-150x150.jpg)
![Best CPU Under 0 - An EPIC Buying Guide [2022] Best CPU Under 0 - An EPIC Buying Guide [2022]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/best-cpu-under-300-150x150.jpg)
![Does CPU Matter For Streaming In 2022? [A Definitive Guide] Does CPU Matter For Streaming In 2022? [A Definitive Guide]](https://maximum-tech.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Does-CPU-Matter-For-Streaming-150x150.jpg)